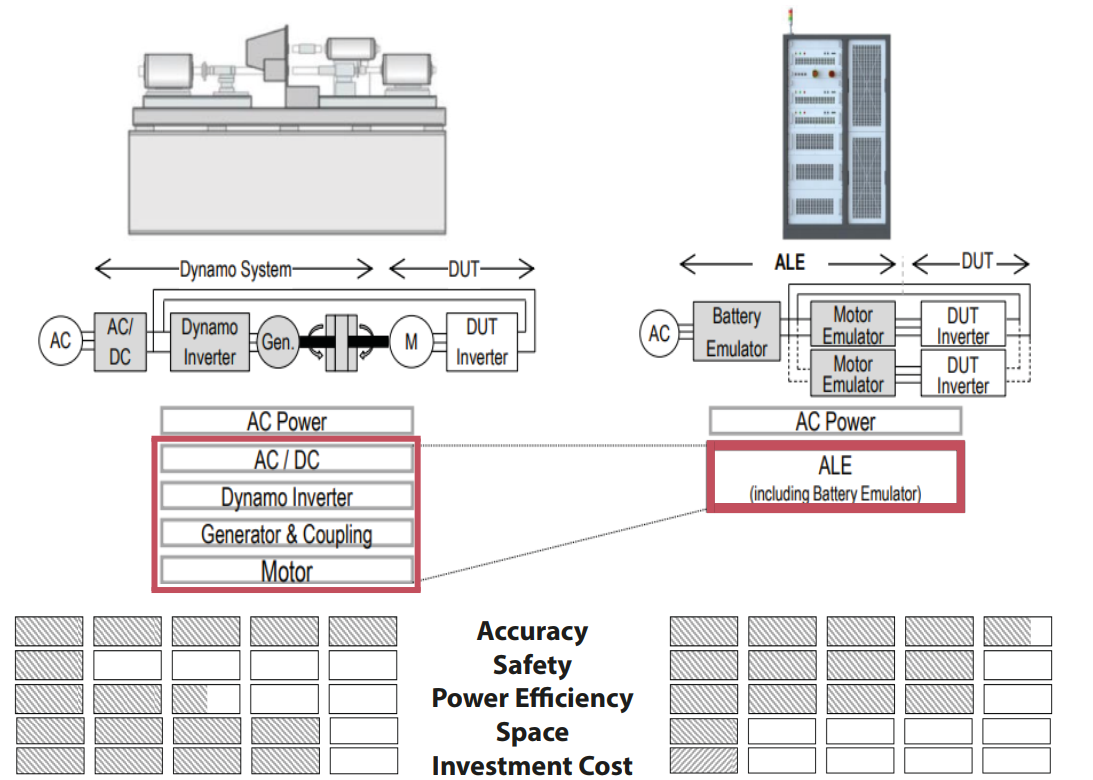
Active Load Emulator
powered by LGE
“The Future of electric vehicle inverter testing”
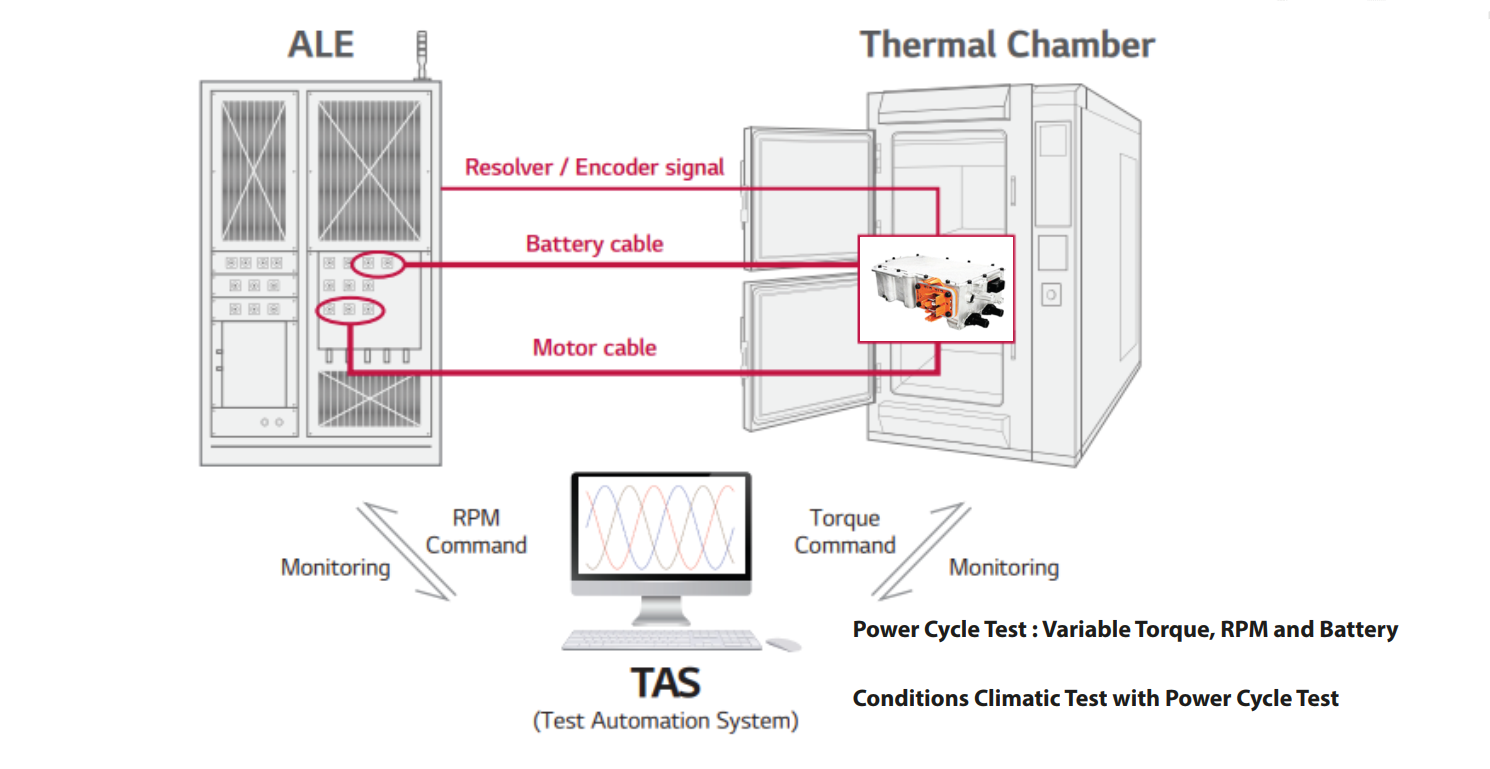
Motoremulering
- Motoremuleringsnoggrannhet över 95 %
- Snabbt svar för vridmoment/rpm variation
- Resolver och kodare gränssnitt
- Systemskydd för olika feltillstånd
- Flerfasig (3,6,12) motor tillämplig (G2.0)
Batterispänningsemulator
- Spänningskälla för utvärderingsomriktare
- Matningsspänning upp till 1000 VDC (G2.0)
Låg investerings- och driftskostnad
- Kompakt design med litet fotavtryck
- Låg initial investering och underhåll
- Hög energieffektivitet
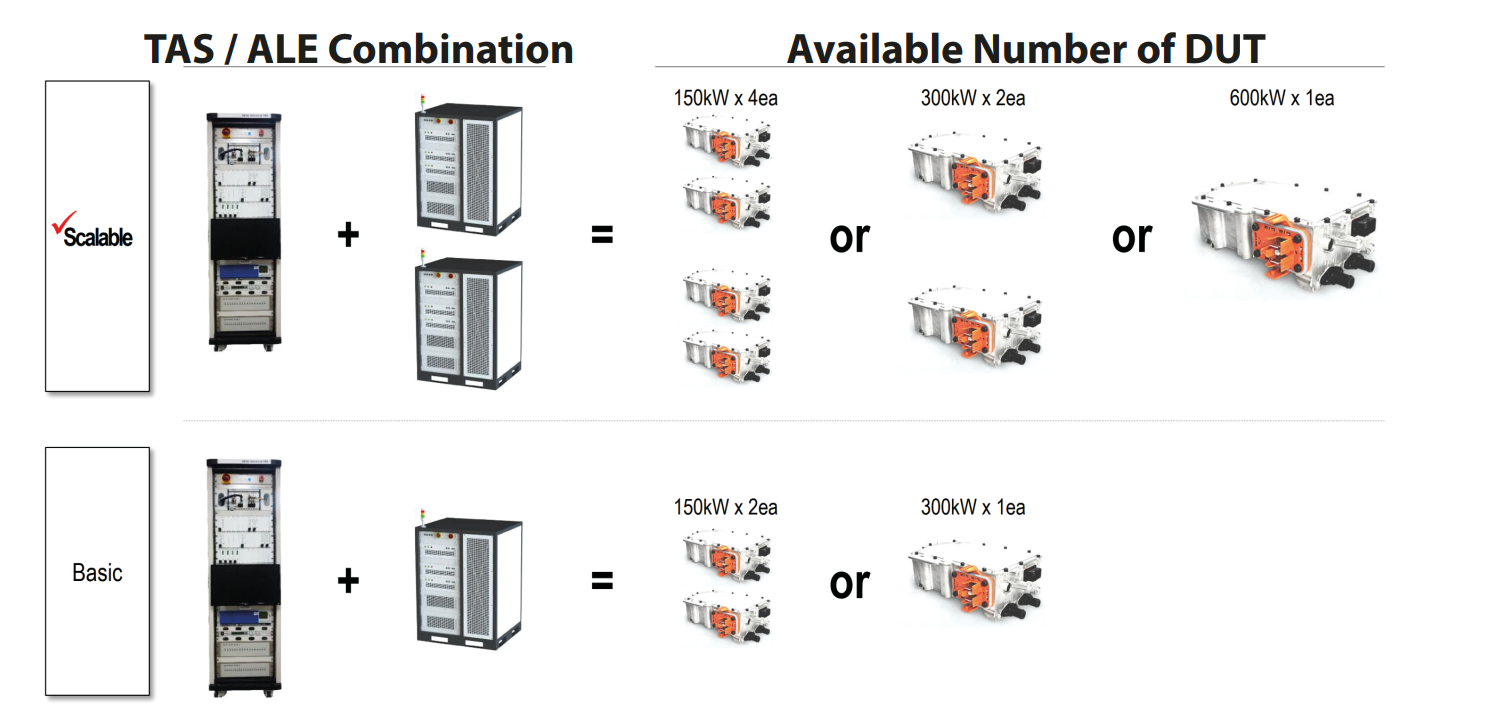
Skalbar effektkapacitet (G2.0)
- Högeffekts invertertest (Max 1,2 MW)
Generel:
| Kategori | G1.0 | G2.0 |
| Dimensioner (BxHxD) | 740 x 2170 x 1150mm | 1250 x 2000 x 1290mm |
| Vikt | 1600kg | 2000kg |
| Effekt | individual kanal 150kW, Parallel 300kW | individual kanal 150kW, Parallel 300kW |
| Kylvätska | DI Vatten eller kompatibel | DI Vatten eller kompatibel |
| Kylvätskeflöde | 45 l/min | 60 l/min |
| IP klass | IP20 | IP20 |
| Service Life | 10 år | 10 år |
Batteri Emulator:
| Kategori | G1.0 | G2.0 |
| Nominell Effekt | 60 kW | 80 kW |
| Utgångs Spänning | 195 - 800 VDC | 195 - 1000 VDC |
| Nominell DC Ström | 240 A | 240 A |
Motor Emulator:
| Kategori | G1.0 | G2.0 |
| Antal Motorer | individuel två, parallel en motor | individuel två, parallel en motor |
| Operativ AC Frekvens | 0 - 800 Hz | 0 - 1500 Hz |
| Individuell AC belastningsström | 400 Arms (Nom) 500 Arms (60s / 10 min stop) | 400 Arms (Nom) 500 Arms (60s / 10 min stop) |
| Parallel AC belastningsström | 800 Arms (Nom) 1000 Arms (60s / 10 min stop) | 800 Arms (Nom) 1000 Arms (60s / 10 min stop) |
| Power Extension | N.A. | Upp till 4 parallel |
| Back EMF | 0 - 480 Vrms | 0 - 612 Vrms |
| Torque direction | P,N | P,N |
| No. Motor Poler | 24 poler | 24 poler |
| Resolver Lobes / Offset | 2 - 24 | 2 - 24 |
| Resolver Excitation Frekvens | 10 - 20 kHz | 10 - 20 kHz |
| Encoder Typ / PPR | N.A. | Incremental (A, B, Z) / 0 - 512 PPR |
| Gränssnitt | CAN 2.0 A | CAN 2.0 A |
ALE G1.0

Ale G2.0

Overview
Skalbarhet
Active Load Emulatorer är också mycket relevanta inom invertertestbänksteknik. En växelriktare är en elektronisk enhet som omvandlar likström (DC) till växelström (AC) eller ändrar frekvens, spänning eller fasvinkel för AC-utgången. Sådana växelriktare används i olika applikationer, inklusive förnybara energikällor som vind- eller solenergi, elfordon, industriella installationer och mer.
Lastsimulering: Växelriktare måste testas under olika belastningsförhållanden för att säkerställa att de kan leverera förväntad prestanda och stabilitet. Active Load Emulatorer möjliggör simulering och testning av uteffekten som produceras av växelriktaren i en kontrollerad miljö.
Krafthårdvara i slingan: På grund av den regenerativa återkopplingen som möjliggörs av användningen av denna teknik, minskar energibehovet avsevärt.
Effektivitetstestning: Effektiviteten hos en växelriktare kan mätas genom att simulera olika belastningsförhållanden. En Active Load Emulator kan belasta växelriktaren med variabla belastningar och utvärdera dess effektivitet över hela driftområdet.
Dynamiska tester: Växelriktare behöver ofta hantera snabba lastförändringar, särskilt i applikationer som elfordon. En Active Load Emulator kan replikera sådana dynamiska laständringar och utvärdera växelriktarens förmåga att reagera snabbt.
Stabilitetskontroller: Växelriktare måste fungera stabilt, utan att orsaka oönskade svängningar eller instabiliteter i systemet. Simulering av olika belastningsförhållanden med Active Load Emulators kan hjälpa till att verifiera växelriktarens stabilitet.
Utveckling och validering: Vid utveckling av nya växelriktare eller uppdatering av befintliga modeller underlättar Active Load Emulators grundlig validering och optimering innan växelriktarna distribueras i verkliga applikationer.
Sammantaget är Active Load Emulators oumbärliga verktyg i invertertestbänksteknik för att analysera och säkerställa prestanda, tillförlitlighet och interaktion hos växelriktare med elnätet eller andra energikällor.






